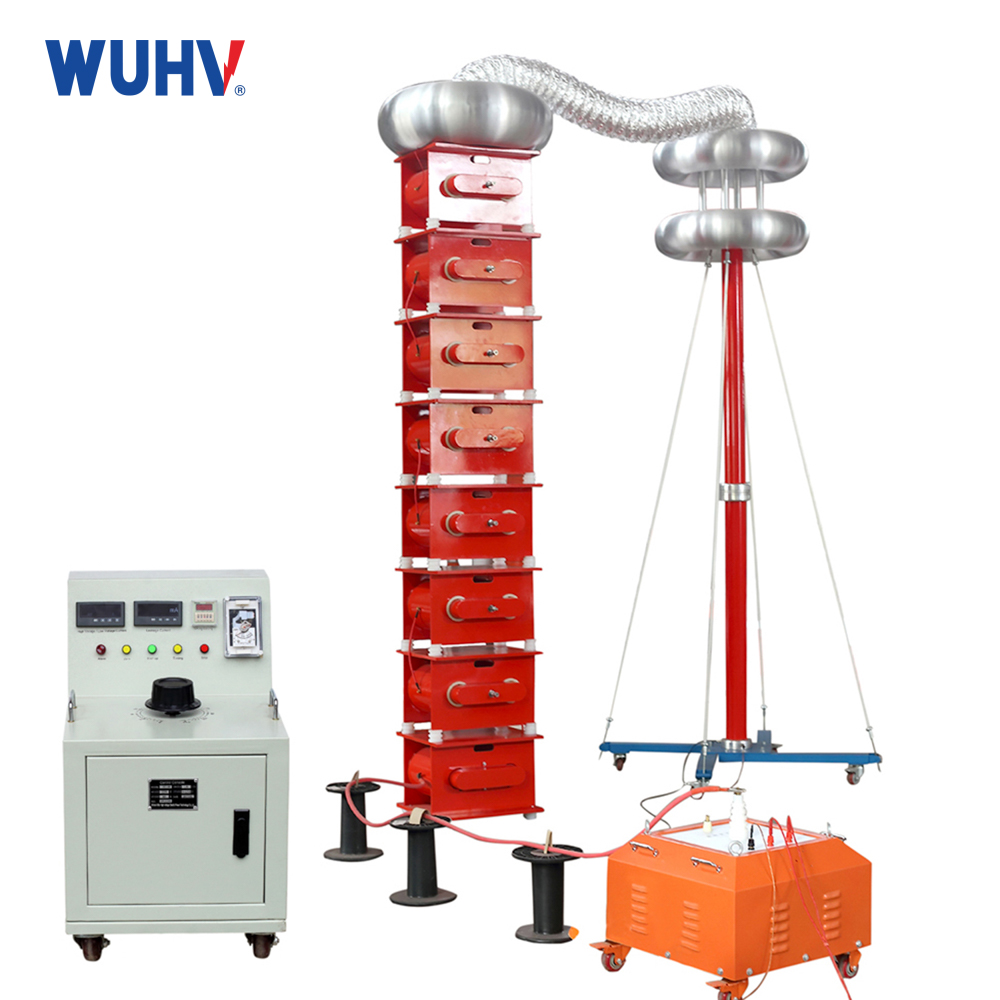
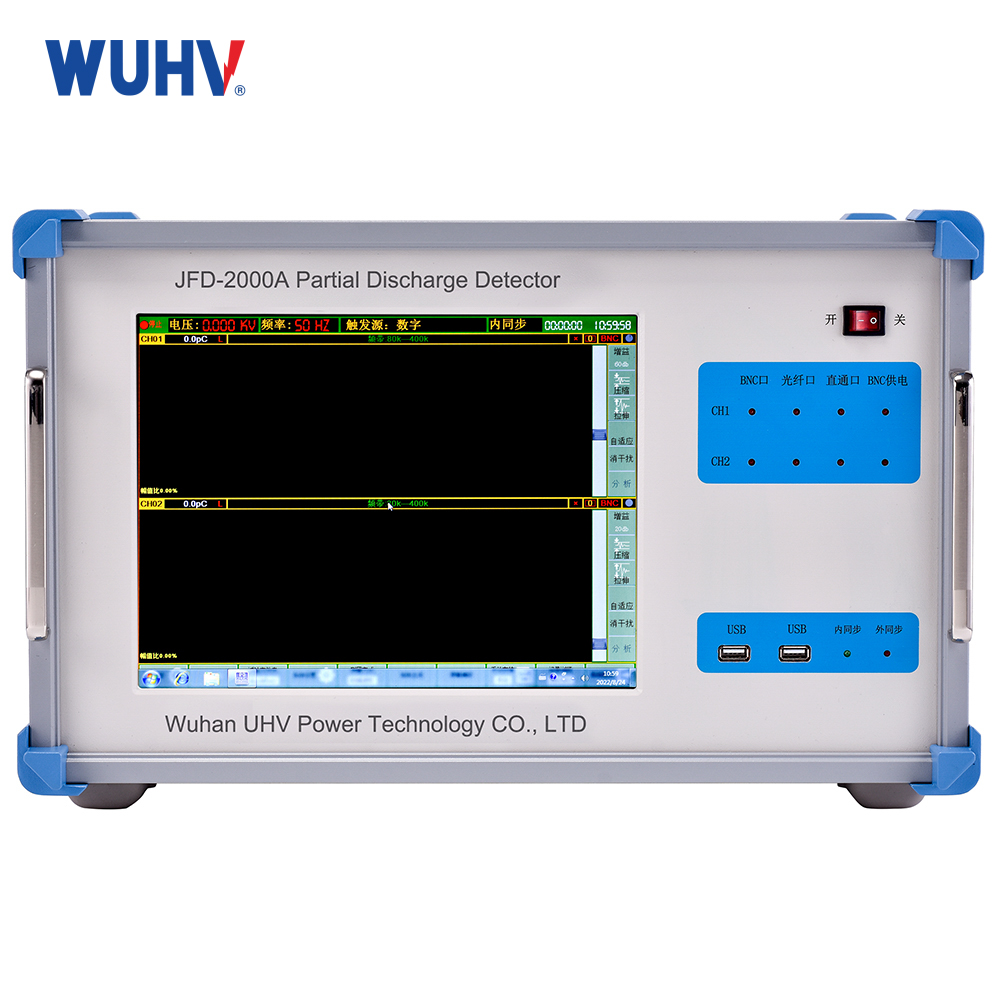
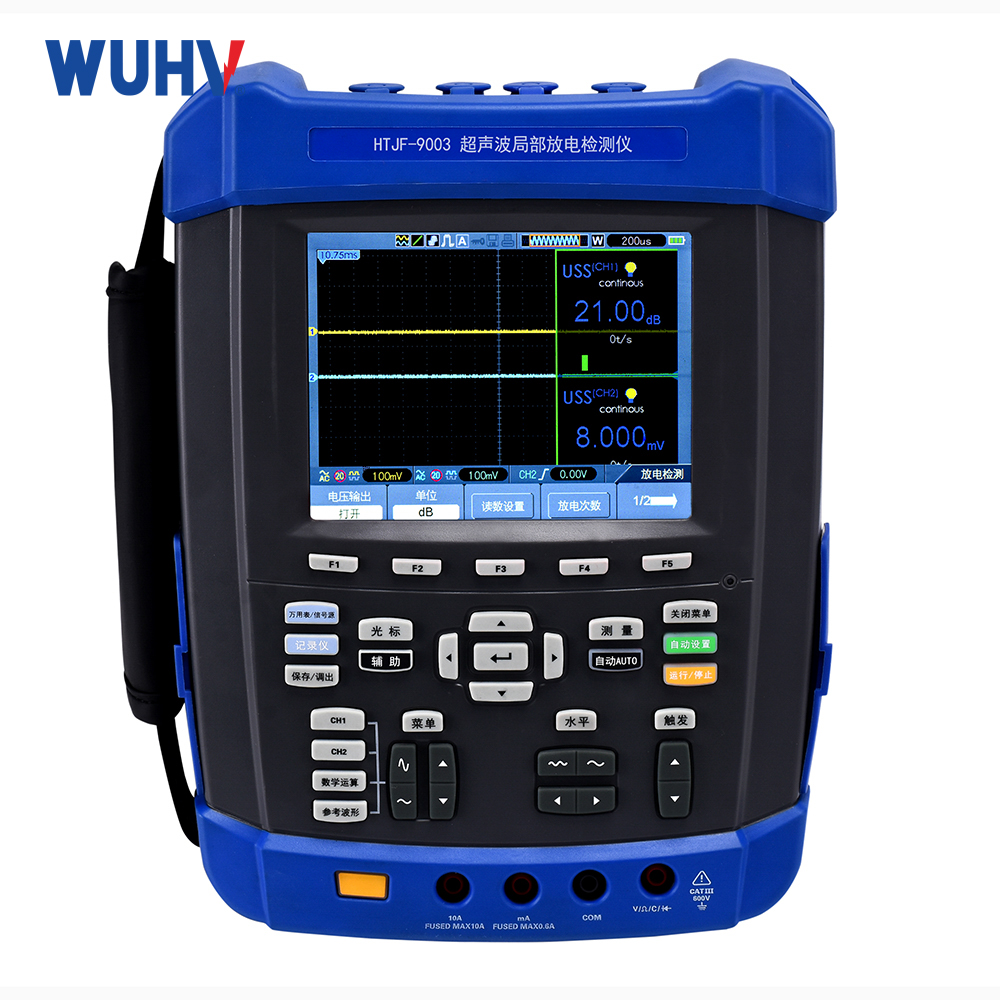
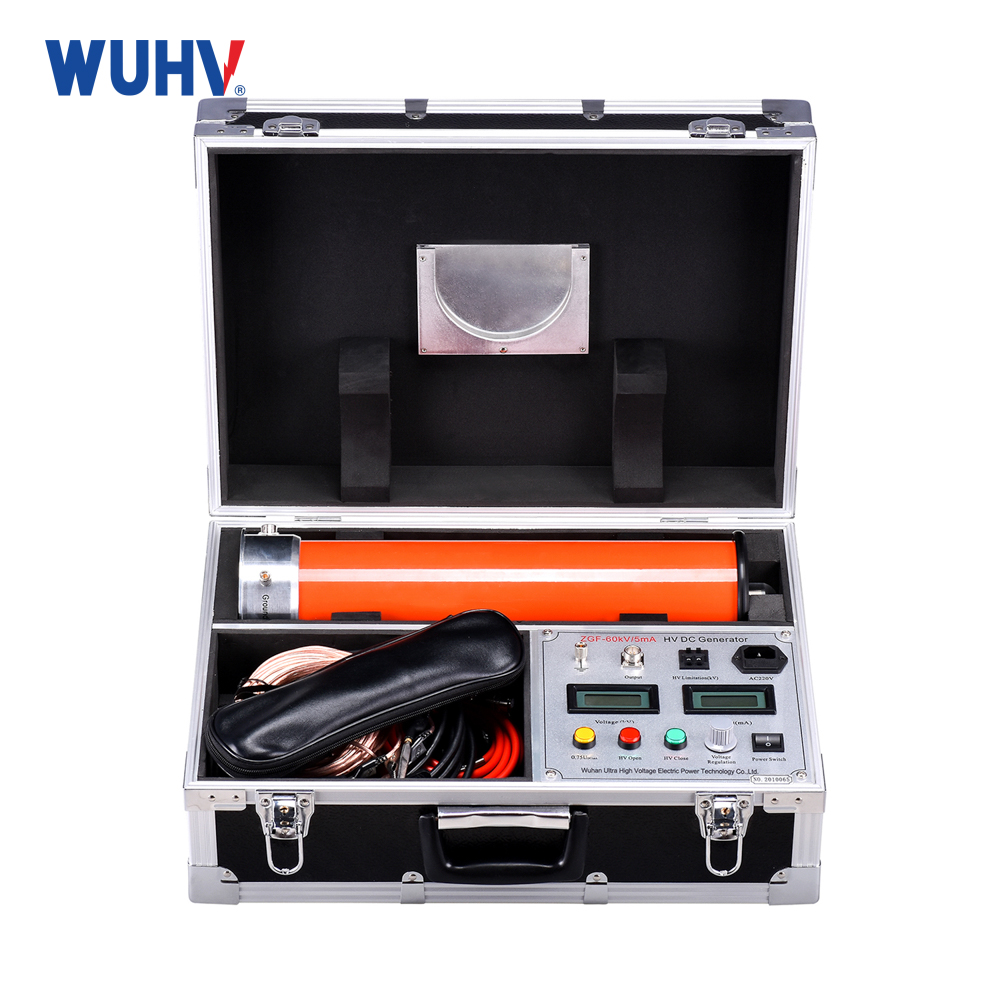
The trace moisture analyzer under UHV power can help many power workers conduct various power tests more conveniently.

The Karl Fischer titration reaction uses volumetric or Coulombic titration to determine the amount of water present in the sample based on the oxidation of sulfur dioxide by iodine, where water is consumed in the buffer solution.
This technology was discovered by Karl Fischer. Karl Fischer titration is a method for determining the moisture content of different types of substances. This depends on the reagent that reacts with the water content and turns it into a non-conductive chemical. Volume KF titration and Coulomb KF titration are two techniques that can be used for Karl Fischer titration of water:
Volumetric Karl Fischer titration: Using this technique, the moisture content depends on the volume or quantity of reagents used to convert water. Volume determination is suitable for measuring the moisture content of water as low as 1%. In these types of KF techniques, the sample is dissolved in a solvent before starting titration until the reagent is removed from water, and then the reagent is added and the endpoint is determined by potentiometry.
In this method, Karl Fischer reagent contains buffer base, alcohol, sulfur dioxide, and identifiable amounts of iodine, which are necessary to reach the titration endpoint.
Coulombic Karl Fischer titration method: The advantage of the Coulombic Karl Fischer titration method is its ability to accurately calculate moisture content. Usually, if the moisture content is less than 1%, this method is used. In this method, the solvent and reagent are mixed in a titration cell, requiring only one iodine containing solution. The anodic oxidation of iodide in solution produces the iodine required for KF reaction, and the endpoint is determined electrochemically.
The amount of iodine added to the sample is calculated by measuring the current demand generated by iodine electrochemistry. When reacting with water, brown iodine solution is reduced to colorless iodide. In this method, sulfur dioxide, iodide ions, alkali, and solvent (alcohol) are used to complete the reaction.