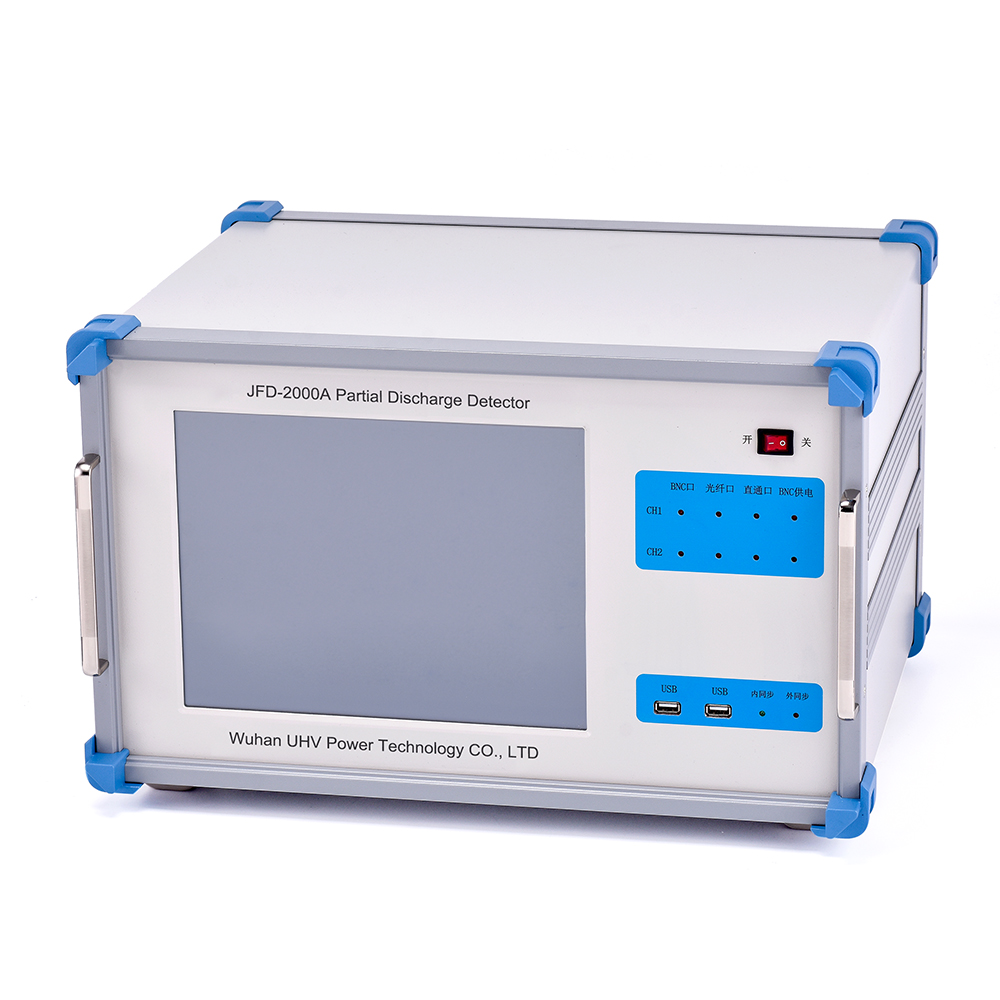
The specialized production of partial discharge testers for UHV power can help many power workers conduct various power tests more conveniently.
What is (partial discharge) PD and why do we need to test it?
PD is a discharge that occurs in a localized area of insulation between two conductive electrodes, without completely bridging the gap (see IEC 60270) It may be caused by discontinuities or defects in the insulation system. PD activity is an indication of early medium voltage (MV) or high voltage (HV) insulation faults and is widely regarded as the best warning indicator for electrical insulation degradation of medium and high voltage electrical assets in power networks. Generally speaking, partial discharge occurs in systems with a voltage of 3 kV or higher; However, it should be noted that in some cases, PD may also occur at lower voltages (i.e. variable speed drive/variable frequency drive motors and LV designs). The typical driving factors for implementing PD plans include: supporting state based maintenance (CBM), avoiding unplanned and often costly interruptions, improving network reliability/uptime, enhancing security and extending asset life/delaying capital replacement (under OPEX budget).
Where did PD occur?
Partial discharge may occur at various points in the insulation system, such as gaps or voids in solid or liquid insulation media, interfaces between insulation layers, such as delamination.
PD can be observed at various stages of the asset lifecycle. From transportation to installation and commissioning of new equipment - usually caused by improper installation or poor design and/or process (especially on-site assembly of cable joints and terminals). Poor manufacturing processes during the asset manufacturing phase may lead to premature failure, with a higher proportion of insulation failures observed in the first 1-3 years of use compared to the remaining working life of the asset. Refer to the bathtub curve below; Partial discharge activity can begin under normal operating conditions of MV/HV assets, where insulation conditions deteriorate over time, or prematurely age due to thermal or electrical overstress or improper installation.
How does PD develop?
Once infected, partial discharge can develop into electrical trees and surface tracking, ultimately leading to faults between phases or between phases of a three-phase system. Depending on the type and location of discontinuities or defects in the insulation system, faults may take several hours to several years to occur.
Although some discharges may be extremely dangerous to the health of insulation systems (such as discharges in polymer cables and cable accessories), other types of discharges may be relatively mild (such as corona entering the air from sharp exposed points on high-voltage overhead networks) The key to partial discharge testing and monitoring is the ability to distinguish between different types of partial discharges that may occur and provide reliable locations, enabling remedial maintenance work to be carried out before faults occur during scheduled power outages, which often result in costly power outages and related downtime or production losses.