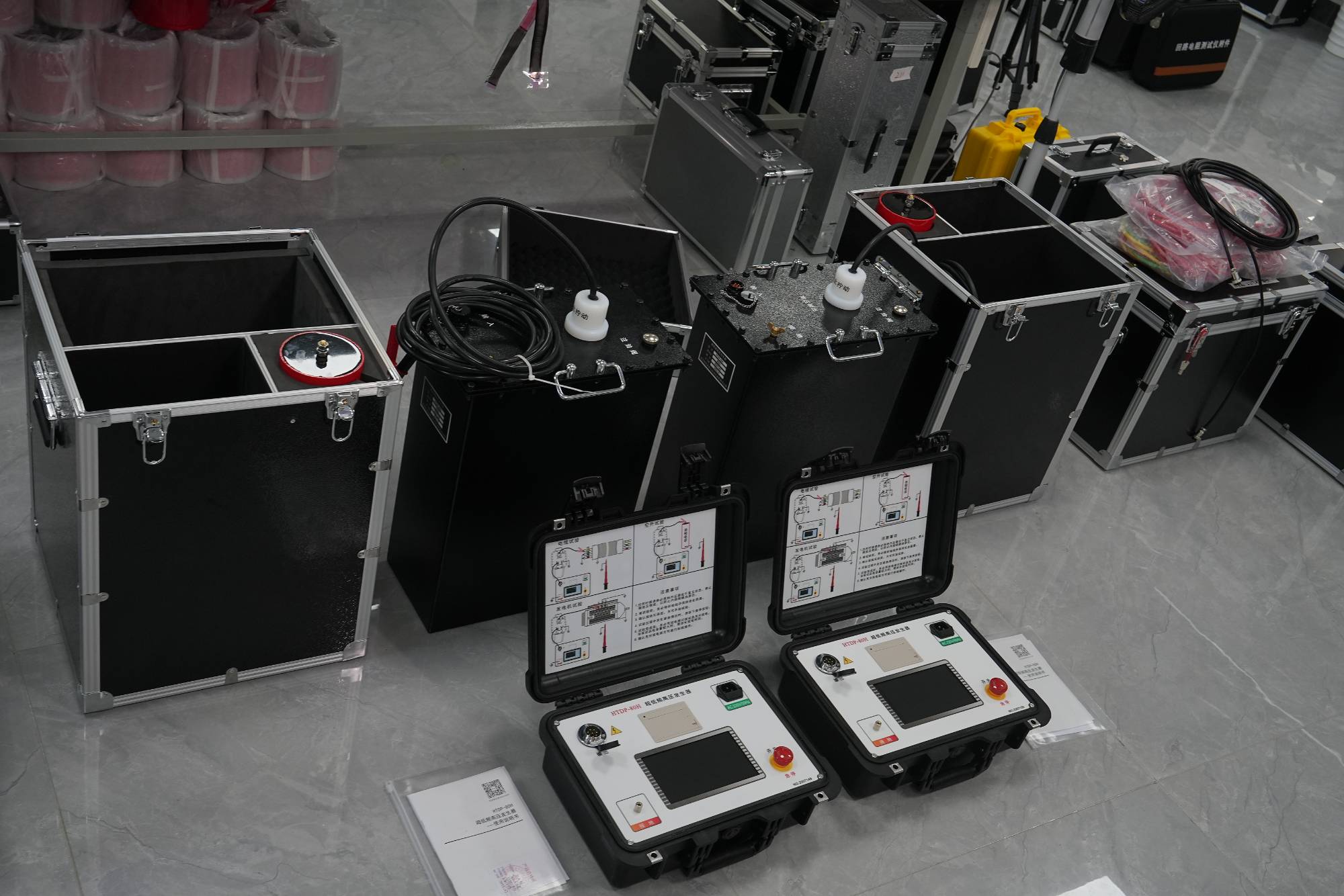
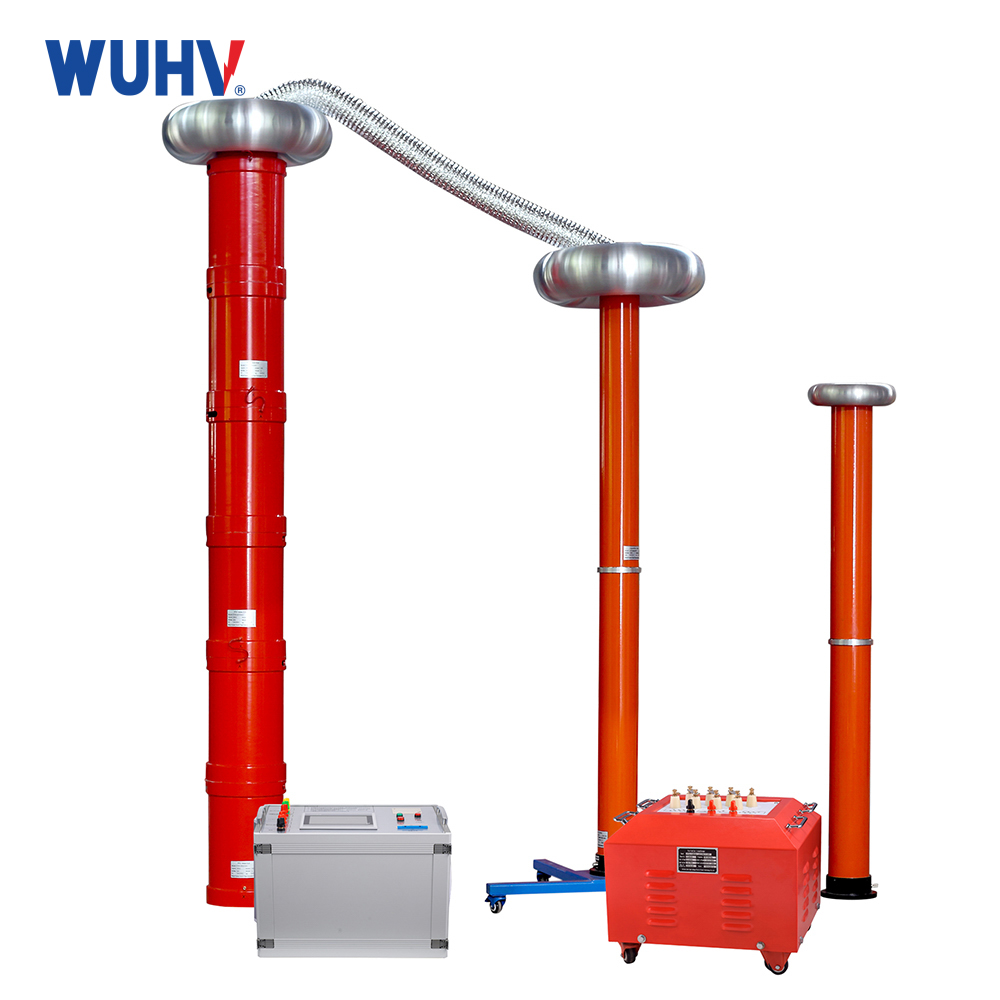
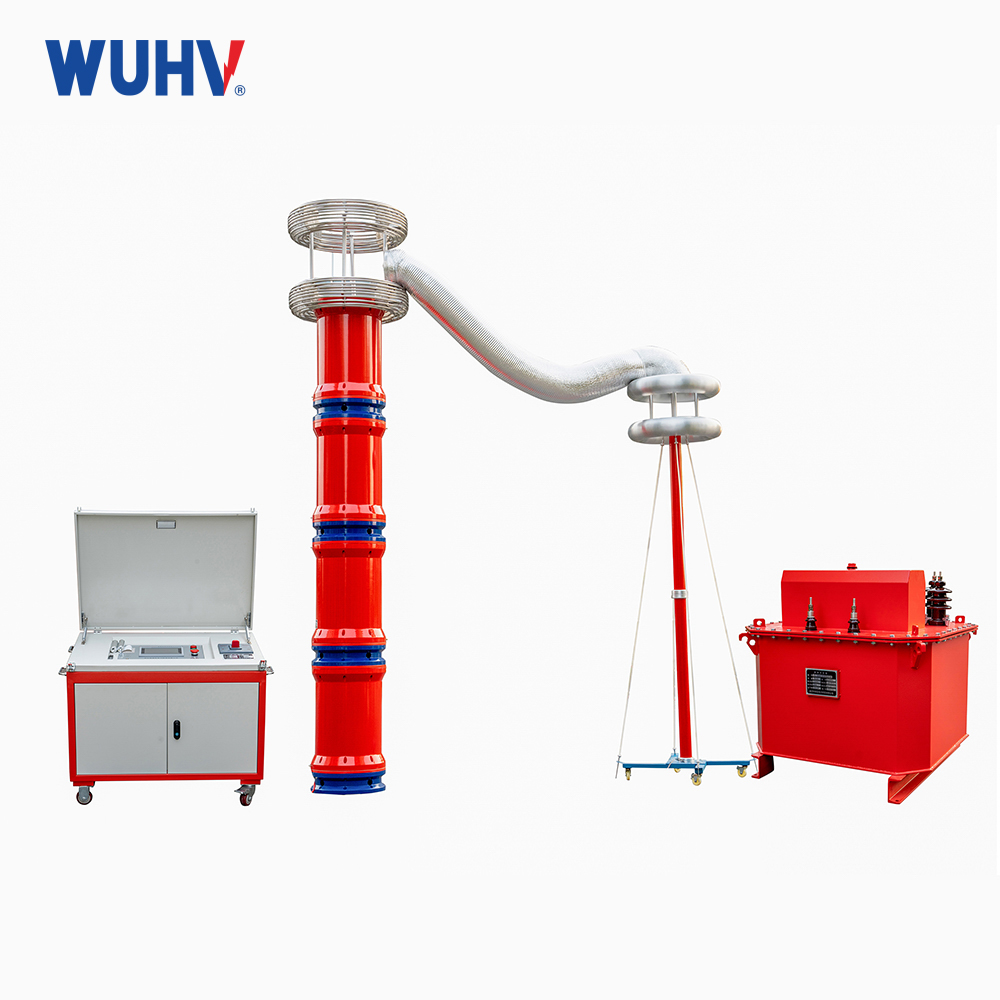
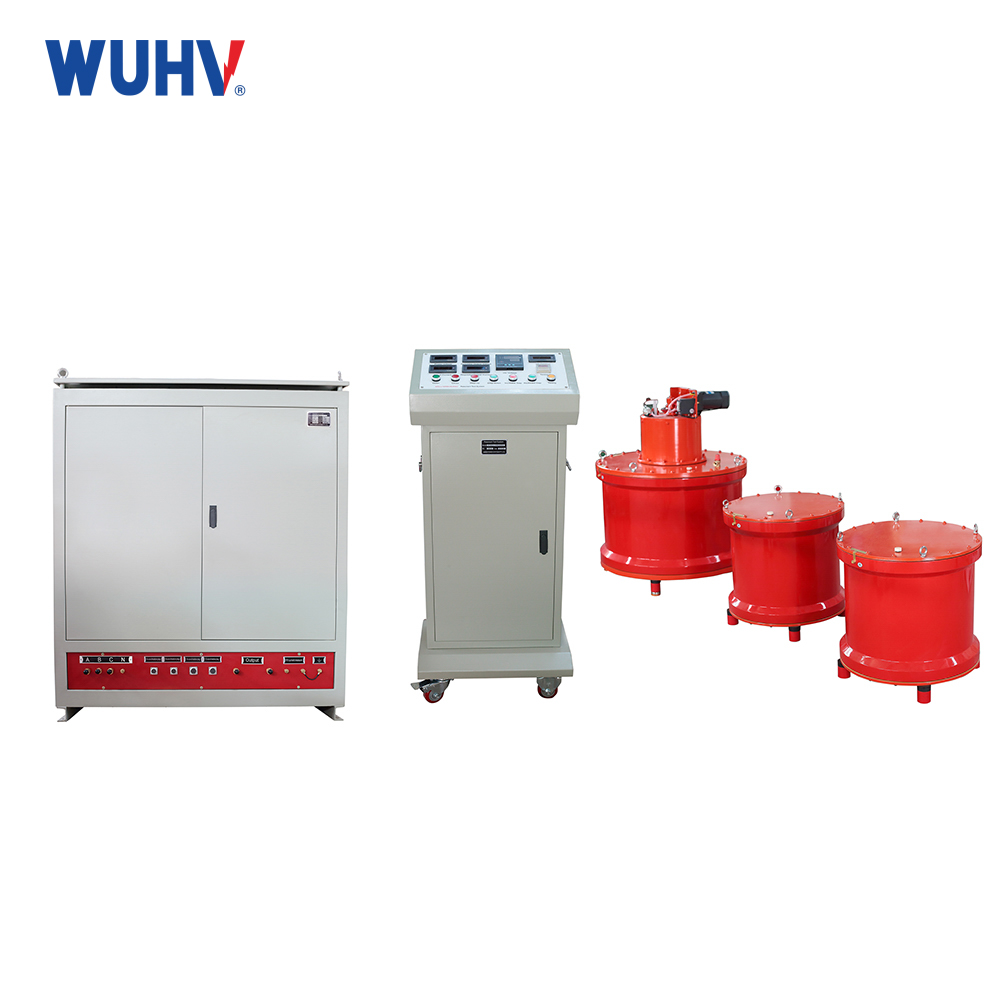
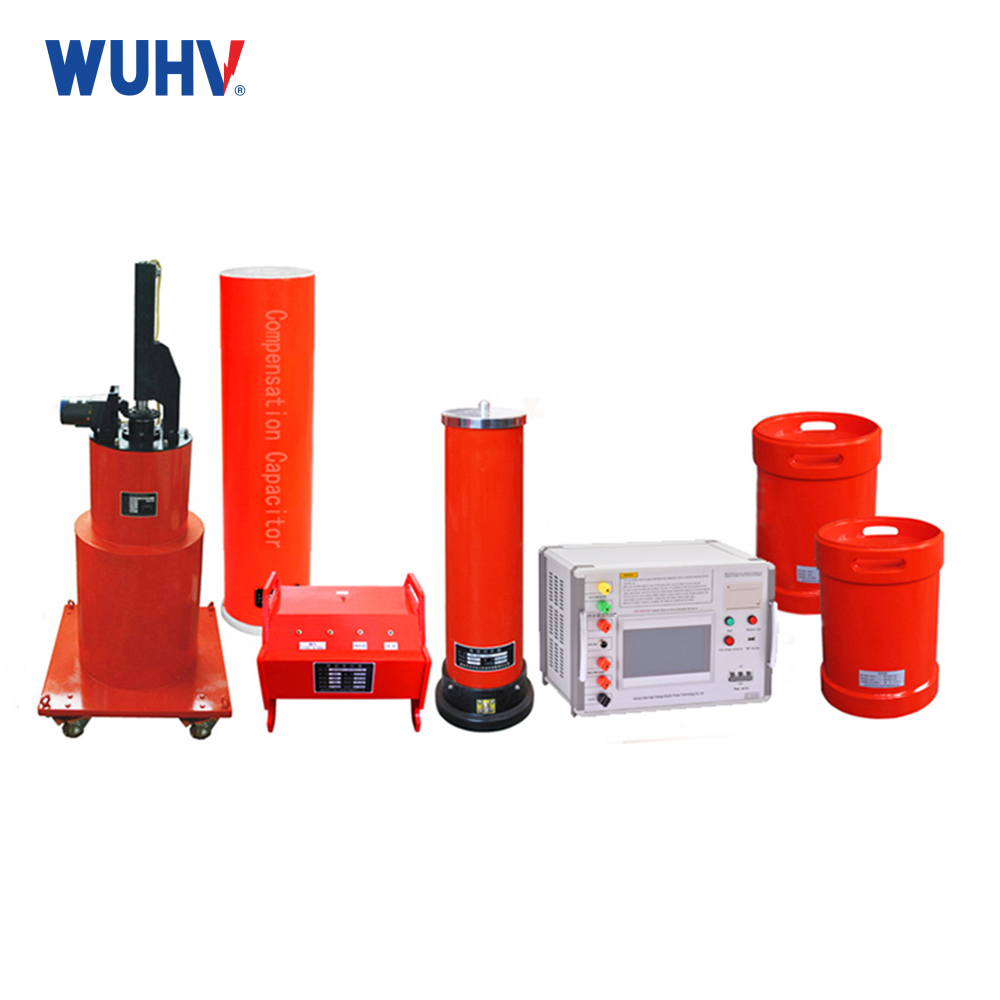
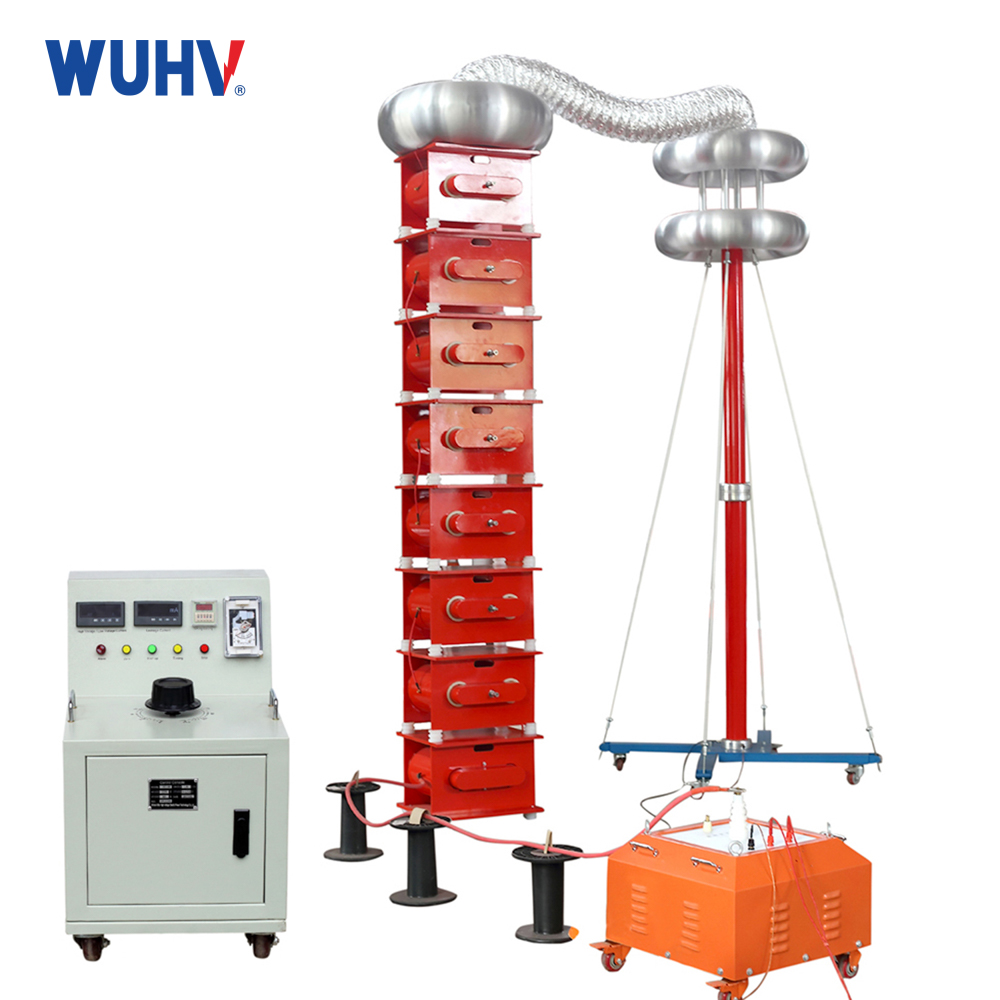
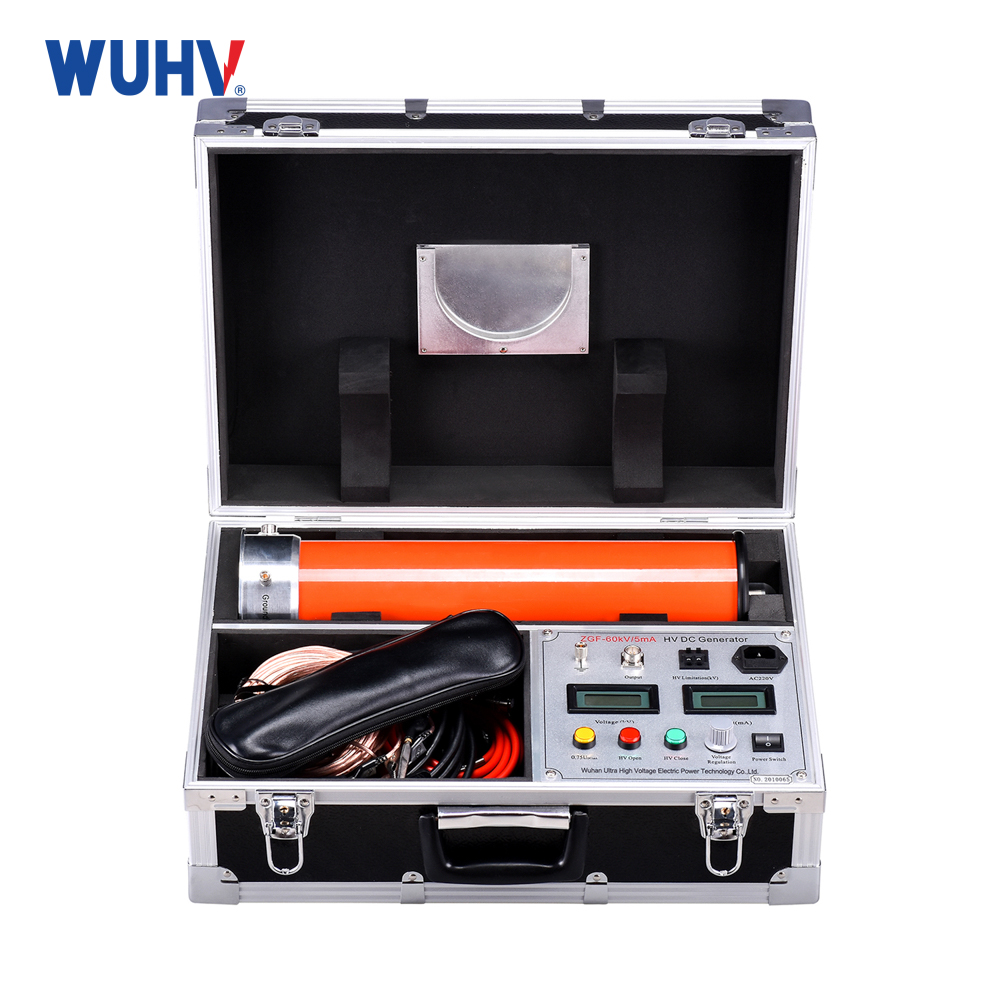
The very low frequency high voltage generator under the UHV power can help many power workers conduct various power tests more conveniently.
Very low frequency high-voltage generators are generally used for voltage withstand tests of power cables and can also be used for insulation voltage withstand tests of large power transformers.
Its characteristic is that it has no damage to the tested cable, and can also test cables that have begun to age but are still usable. It is a non-destructive voltage testing method.
This test more accurately determines the connection errors of new and repaired cables at their joints and ends than DC high voltage testing.
Industry standard "Test method for very low frequency (0.1Hz) voltage of xLPE insulated power cables below 35kV". According to the requirements of this industry standard, the testing procedure is as follows:
All electrical equipment connected to the test product should be separated from the test cable, and the test equipment (very low frequency high voltage generator, etc.) should be reliably grounded with bare copper wire.
Use a 10000V megohmmeter to test the insulation resistance of each phase of the cable and record the test values.
Peak test voltage: 3VO, test time: 60min.
When the capacitance of the test cable is within the load capacitance range of the testing equipment, the three-phase cores of the test cable can be connected in parallel and subjected to a withstand voltage test.
Connect the testing equipment to the testing cable using a flexible connection cable, turn on the power, and start the boost test. During the boosting process, the high-voltage circuit should be closely monitored to check for any abnormal noise from the testing cables. When the test voltage is reached, start recording the test time and reading the test voltage.
After the testing time, first reduce the voltage to zero, and then cut off the power supply. If no destructive discharge occurs during the experiment, it is considered to have passed the voltage test.
During the pressurization process, if the pressure pointer of a voltmeter swings significantly and the ammeter indicates a sharp rise in voltage to the point where the boosted voltage basically stops or drops, and the current rises significantly, or if there is any abnormal phenomenon such as odor, smoke, abnormal noise, or flashing in the test cable, the boosting should be stopped immediately. After identifying the cause, the voltage should be reduced and the power should be cut off. If these phenomena are found to be caused by the weak insulation of the test cable, it is considered that the voltage test is not qualified. If it is determined that the test cable is caused by humid air or dirty surface, the test cable should be cleaned and wiped dry before testing.
During the testing process, if an unexpected power outage is caused by insulation defects in the non test cable, resulting in a test interruption, the full-time connection should be re established after identifying the cause and restoring power supply.