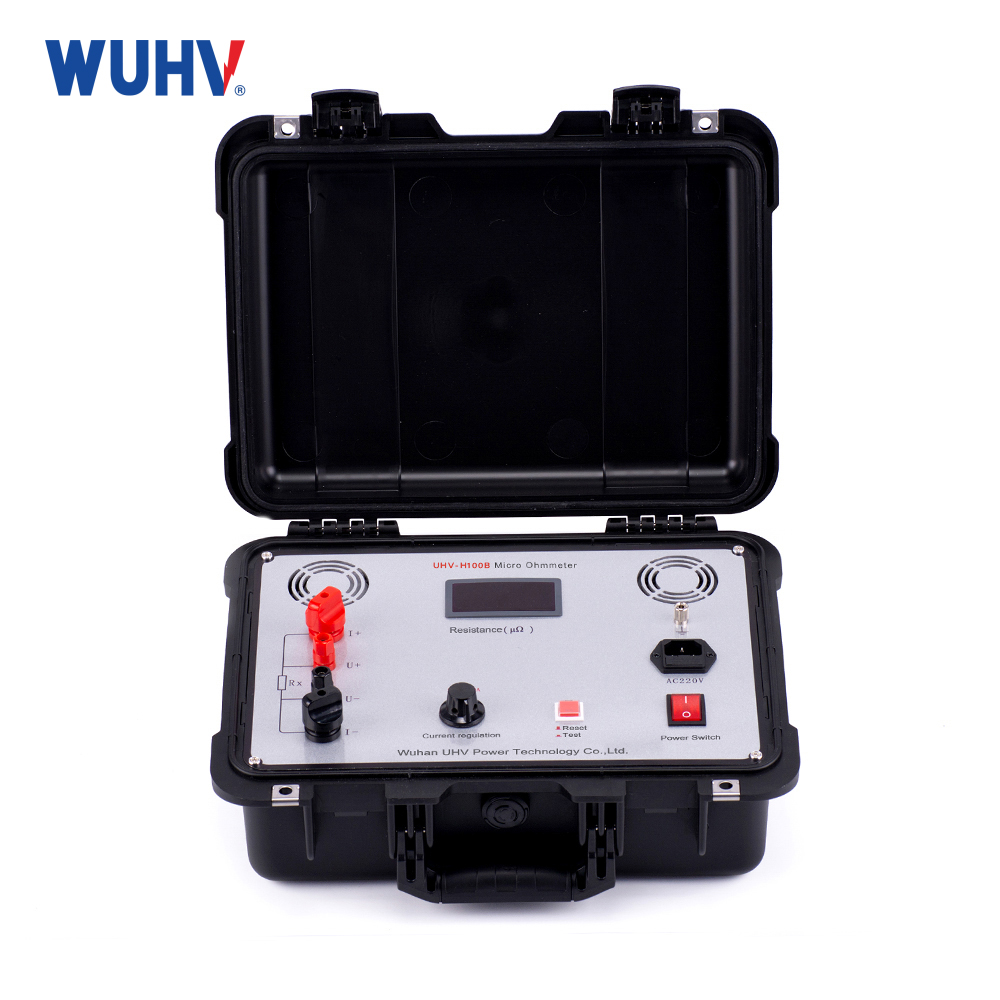
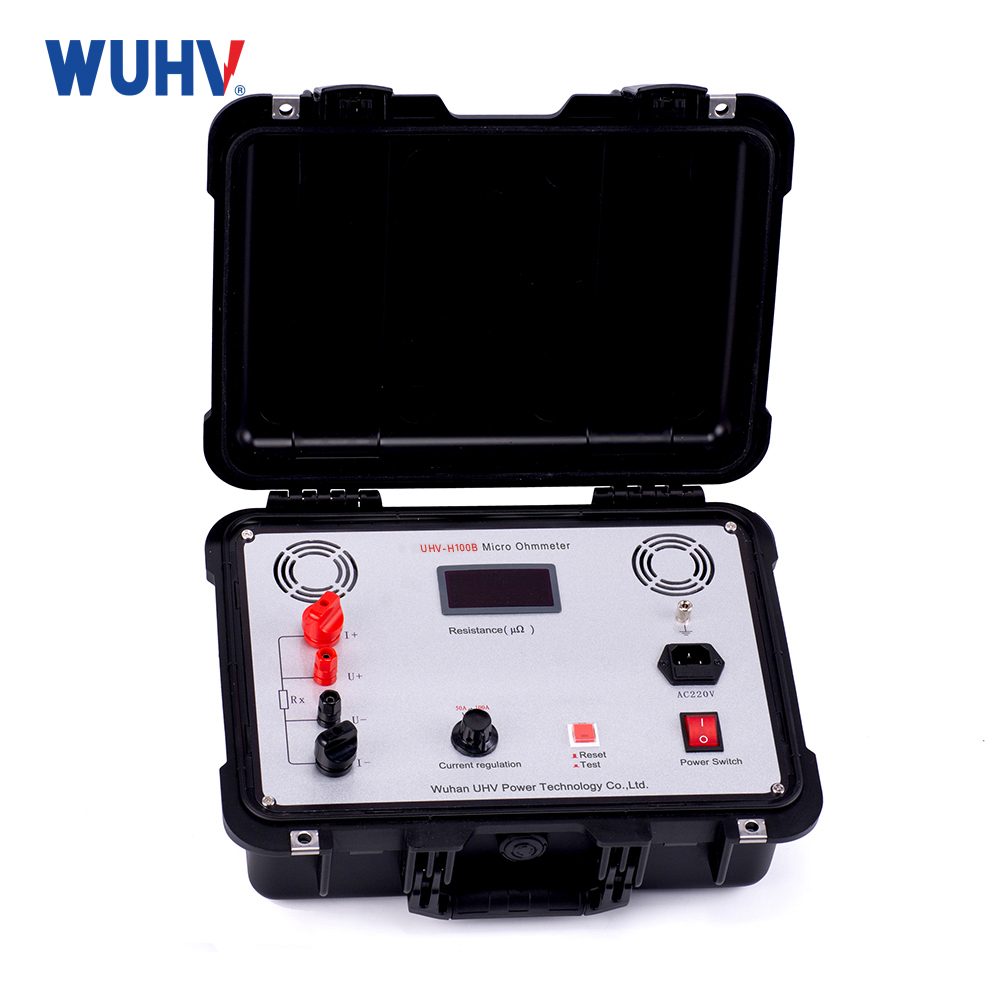
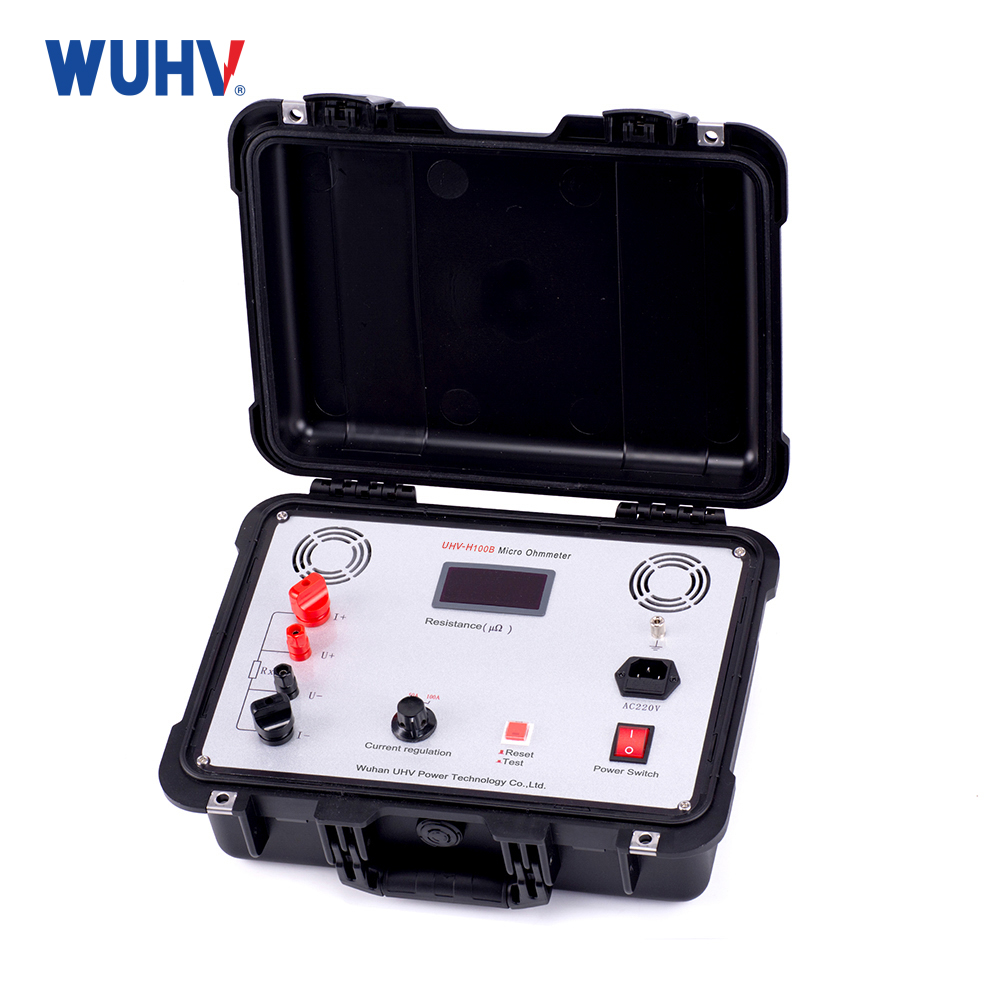
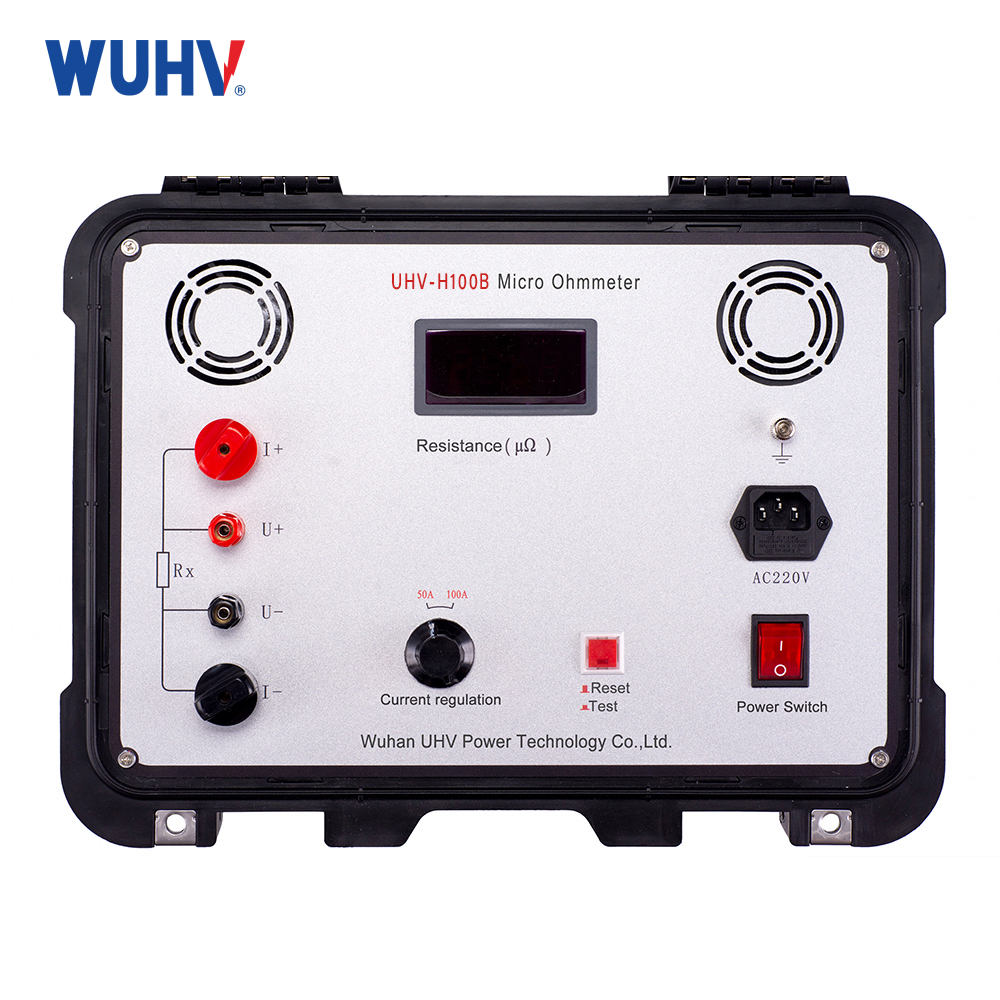
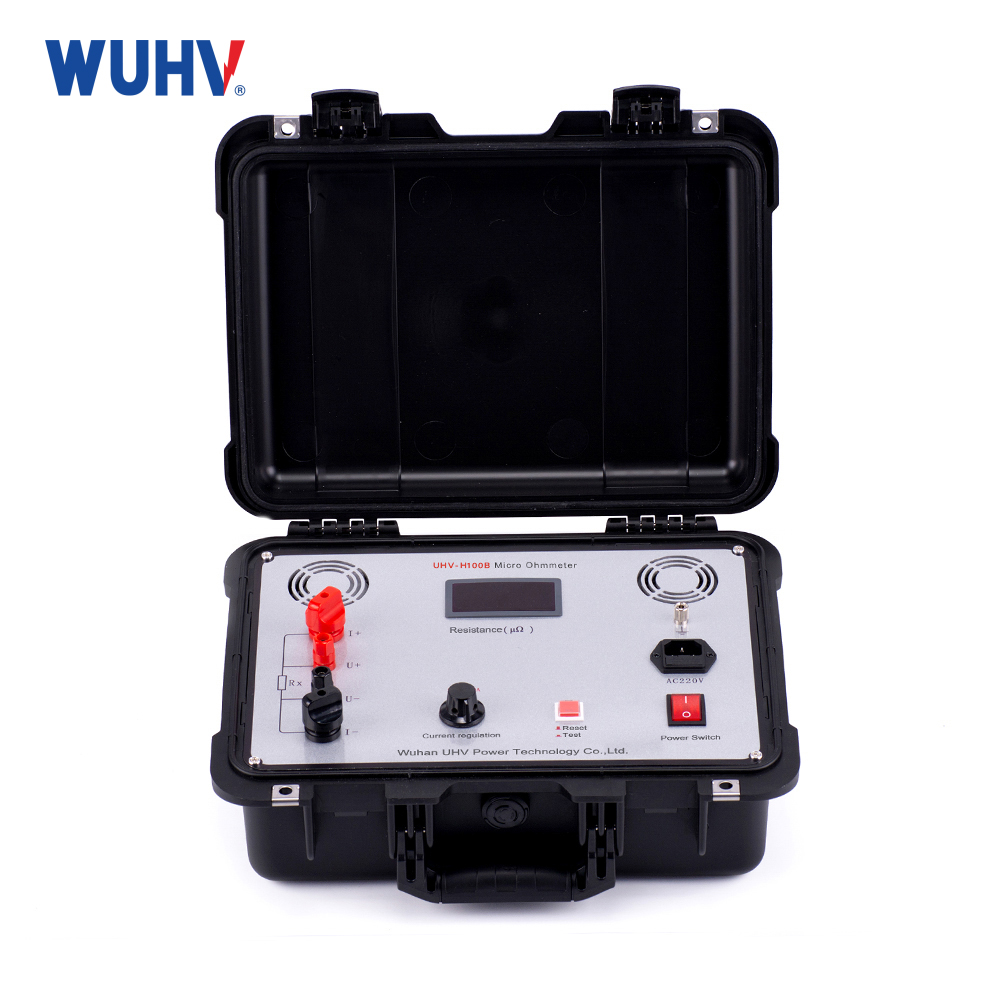
Technical parameters
measuring range | 1~1999μΩ |
resolving power | 1μΩ |
Test current | DC 100A fixed output |
measurement accuracy | 0.5%±1d |
operation mode | continuity |
Display mode | Three and a half digit digital tubes |
Working power supply | AC220V±10% 50Hz |
work environment | Temperature: -10 ℃~40 ℃, humidity: ≤ 80% RH |
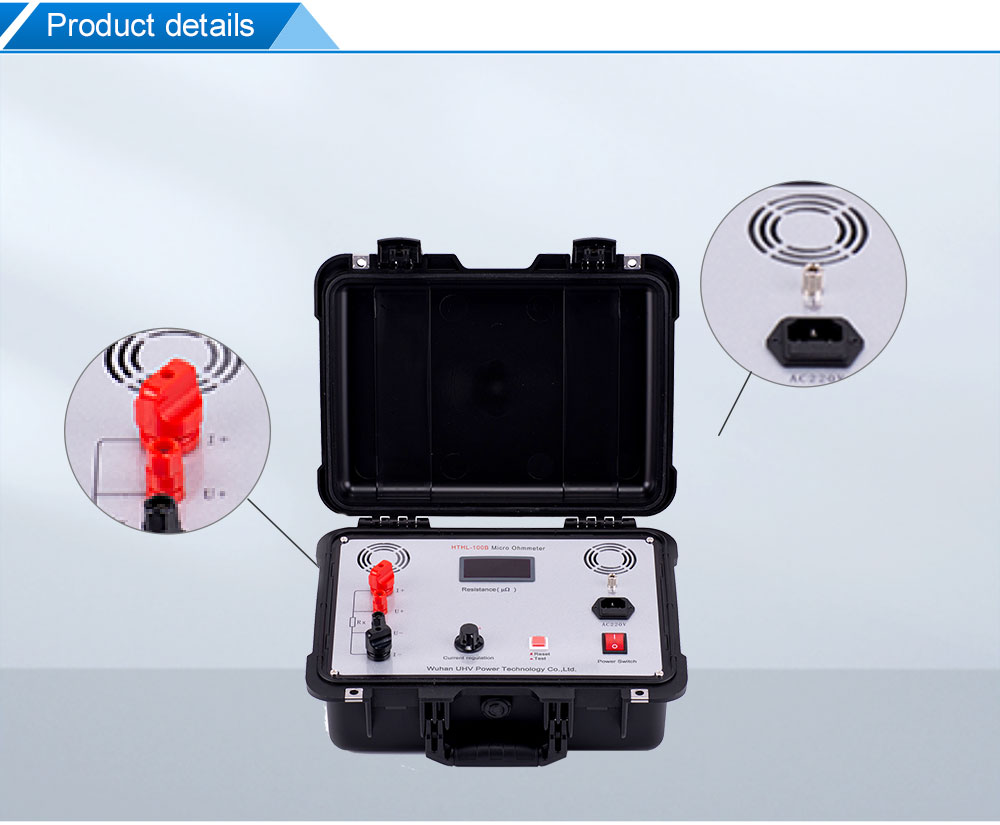



matters needing attention:
1. Please read the instruction manual carefully before using the instrument.
2. Please follow the correct wiring method in the instruction manual to connect the wires.
3. This instrument is not allowed to test the circuit resistance in live circuits.
4. The instrument must be reliably grounded during use.
5. Current line users are not allowed to replace them at will.
6. When not in use, the instrument should be stored in a ventilated, dry, cool, and clean place, paying attention to moisture and corrosive gases.
Basic knowledge of contact resistance:
1. What is contact resistance?
Contact resistance is the additional resistance that occurs when a stationary contact comes into contact with a moving contact.
2. What are the components of the contact resistance of a circuit breaker?
It consists of two parts: the contraction resistance and surface resistance of the contact parts of the moving and stationary contacts.
3. What are the reasons for the unqualified contact resistance of the circuit breaker?
1) When breaking a large short-circuit current, the contact burns out.
2) Due to poor institutional adjustment and unstable fixation, the stroke changes. When the overtravel is severely unqualified, it can cause changes in contact pressure or contact area.
3) After the debugging and installation of the circuit breaker, if it is not put into operation for a long time, the surfaces of the moving and stationary contacts will oxidize and the contact surface resistance will increase.
4) Long term operation causes the spring to deform, resulting in a decrease in contact pressure.
5) Mechanical wear caused by long-term operation of mechanical parts.
6) For low oil circuit breakers, it is also possible for the insulation oleic acid value to be unqualified and cause acidic reactions, which can corrode the contact surface. Or floating impurities in the oil, caused by the interruption of short-circuit current between the moving and stationary contacts. The residual carbonaceous particles and metal powders increase the contact resistance.
4. What are the factors that affect contact resistance?
1) - Material properties: resistivity, hardness, chemical properties, mechanical strength and resistivity of metal compounds.
2) Contact forms: point contact, line contact, surface contact.
3) Contact surface condition: When an oxide film is formed on the contact surface (except for silver), the resistance of the oxide film is much higher than that of the metal itself.
4) Contact pressure.
5) Surface roughness of contact